What is the R-Value of Fiberglass Insulation?
Confused by the term "R-value" when shopping for insulation? You’re not alone. It’s the most important number on the package, but it’s often poorly explained, leaving you unsure if you’re making the right choice for your home and budget.
The R-value of fiberglass insulation typically ranges from R-2.9 to R-4.3 per inch of thickness. A standard 3.5-inch batt for a 2×4 wall has an R-value of around R-11 to R-13, while thicker batts for attics can reach R-38 or higher.

Choosing the correct R-value is about more than just picking the highest number; it’s about optimizing your home’s energy efficiency based on your specific climate and needs. As a company that has been manufacturing and exporting world-class insulation since 1998, we at HUAYUE have helped thousands of clients understand this crucial metric. Let’s demystify R-value so you can make an informed decision that saves you money for years to come.
WHAT IS INSULATION R-VALUE?
Are you tired of hearing the term "R-value" without a clear explanation of what it means for you? It’s a technical term that gets thrown around a lot, but its meaning is actually quite simple.
R-value is a measure of thermal resistance, or how well a material stops the flow of heat. A higher R-value indicates better insulating performance. Think of it as the insulation’s power to keep your home warm in the winter and cool in the summer.
Deeper Dive into Thermal Resistance
The "R" in R-value literally stands for Resistance. This value quantifies how effectively a specific material resists the transfer of heat. Heat naturally moves from a warmer space to a cooler one, and insulation’s job is to slow this process down as much as possible. The R-value is determined primarily by the type of material, its thickness, and its density. For fiberglass insulation, the magic lies in the millions of tiny air pockets trapped between the fine glass fibers. These air pockets are what actually do most of the insulating, as still air is a very poor conductor of heat.
So, a thicker batt of fiberglass insulation will have more trapped air and therefore a higher R-value. For example:
- A 3.5-inch thick batt designed for a 2×4 wall might be R-13.
- A 6.25-inch thick batt for a 2×6 wall might be R-19.
- A 12-inch thick batt for an attic might be R-38.
The final R-value of a wall or ceiling system is the sum of all the components, but the insulation provides the vast majority of the thermal resistance.
DETERMINING THE RIGHT R-VALUE?
Are you worried about choosing the wrong R-value and wasting money? You don’t want to over-insulate and pay for performance you don’t need, but under-insulating can lead to high energy bills.
The right R-value for your home depends almost entirely on two factors: your geographical location (your climate zone) and the specific part of the house you are insulating (attic, walls, or floors). The colder your climate, the higher the recommended R-value.

Locate Your Climate Zone To Determine Insulation R-Value
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has simplified this process by creating a climate zone map. The country is divided into 8 zones, and each has a different set of recommended R-values. Finding your zone is the first step to determining your needs.
First, identify your zone on the map below. Then, use the corresponding chart to find the DOE’s recommendations for your area. For example, a home in Zone 2 (e.g., Houston) has very different needs than a home in Zone 6 (e.g., Chicago).
Once you know your zone, you can consult this chart for common recommendations for retrofitting an existing home:
| Climate Zone | Attic | Walls (Wood Frame) | Floors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zone 1 (Hot-Humid) | R-30 to R-49 | R-13 to R-15 | R-13 |
| Zone 2 (Hot-Dry/Humid) | R-30 to R-60 | R-13 to R-15 | R-13 |
| Zone 3 (Warm-Dry/Humid) | R-30 to R-60 | R-13 to R-15 | R-19 |
| Zone 4 (Mixed-Dry/Humid) | R-38 to R-60 | R-13 to R-15 | R-25 |
| Zone 5 (Cool-Dry/Humid) | R-49 to R-60 | R-13 to R-21 | R-25 to R-30 |
| Zone 6 (Cold-Dry/Humid) | R-49 to R-60 | R-13 to R-21 | R-25 to R-30 |
| Zone 7 & 8 (Very Cold/Subarctic) | R-49 to R-60 | R-21 | R-30 to R-38 |
These recommendations from ENERGY STAR provide a reliable target for maximizing your home’s energy efficiency. As a manufacturer, we produce insulation in all these R-values to meet the needs of projects across every climate zone.
HOW DO YOU ESTIMATE HOW MUCH MORE INSULATION YOU’LL NEED?
Worried that your attic doesn’t have enough insulation but not sure how to check? It’s a common problem in older homes, leading to drafts and high energy bills.
To estimate your needs, first determine your existing R-value by identifying the insulation type and measuring its depth in inches. Then, subtract this number from the recommended R-value for your climate zone. The result is the R-value you need to add.
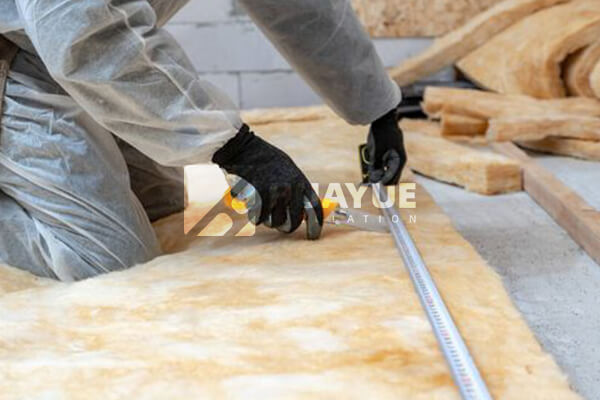

Deeper Dive into an Insulation Audit
Performing a quick insulation check is easier than you think. You just need a ruler or tape measure and a flashlight. Head up to your attic and find a spot where you can see the insulation clearly.
- Identify the Type: Is it batts (blankets) or loose-fill (blown-in)? Most likely it’s fiberglass (pink, yellow, or white) or cellulose (greyish).
- Measure the Depth: Stick the ruler down into the insulation until it touches the drywall of the ceiling below. Read the measurement in inches. Be careful not to compress the insulation.
- Calculate Existing R-Value: Use this simple formula to get a rough estimate:
- Fiberglass (Loose-fill or Batts): Depth in inches x 2.9 = Existing R-Value
- Cellulose (Loose-fill): Depth in inches x 3.7 = Existing R-Value
For example, if you live in Climate Zone 5 and the DOE recommends an R-49 for your attic, but you only have 7 inches of old fiberglass, your calculation would be:
7 inches x 2.9 = R-20.3(Your current insulation level)R-49 (Recommended) - R-20.3 (Existing) = R-28.7
This means you need to add approximately R-30 of new insulation on top of your existing layer to meet the current energy efficiency guidelines.
Conclusion
In summary, the R-value of fiberglass insulation is a direct measure of its heat-blocking power. Choosing the right R-value based on your climate zone is the most critical step for an energy-efficient home.
As a leading insulation manufacturer and supplier since 1998, HUAYUE Group provides a full range of glass wool, rock wool, and other insulation products to meet any R-value specification for projects worldwide.
You may also be interested in:
Ready to Get Started?
Get in touch with our experts for personalized solutions tailored to your needs.
Get Free QuoteLatest Articles
Let's Work Together
Ready to take your business to the next level? Get in touch with our team of experts and let's discuss how we can help you achieve your goals.
Get Free Solutions







